Research Highlights
During the past several years, student and faculty researchers from RK University have published their experimental findings in renowned journals with a Clarivate Analytics Impact Factor - Web of Science Group (JCR) and/or with a SCImago Journal Ranking (SJR). Both of these journal metrics have been globally accepted by the scientific community. India’s National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) gives special emphasis on these two widely accepted metrics. The Faculty of Doctoral Studies & Research (FDSR) at RK University encourages researchers to submit their manuscripts only to those journals that have these two metrics. Following list is recent research paper publications of RK University.
PUBLICATIONS (2019–2020)

Dr. Vipul Patel (Associate Professor, School of Pharmacy, RK University), has been awarded the prestigious “Trend Setter” Award by the Gujarat Innovation Society for his innovation in the area of Diaper Technology for Agriculture. This innovation involves the use of a solid hydrogelling system, which reduces the consumption of water and fertilizers. Dr. Patel has previously received a research grant from the Gujarat Council on Science & Technology (GUJCOST). To learn more about the Gujarat Innovation Society, readers are encouraged to visit http://www.gisindia.org.in/about.html
ABOUT THE TREND SETTER AWARD
Researchers who demonstrate out-of-the-box thinking and adopt unconventional paths are nominated for this award. Innovators whose unique innovations benefit society at large and set up a trend are strongly considered for this prestigious award.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
India ranks 41st among 181 countries with irrigation-related issues. More than 60% of the net cultivable area faces dry land conditions. Every year, over 30% of the agricultural area faces the problem of insufficient rainfall. Because water utilization is less in the industrial (15%) and domestic (5%) sectors as compared to the agricultural sector (85%) and because there is no scope to further reduce the water supply to domestic and industrial areas, the current focus is on optimizing the available water resources for agriculture, to facilitate crop production.
Hydrogels absorb more than 400 times their weight in water. When the surroundings begin to dry out, the hydrogel gradually dispenses up to 95% of its stored water. When exposed to water again, it rehydrates and stores water once again. Hydrogels can be developed by modifying conventional polymers. Such modifications dramatically reduce the cost and improve the gelling strength. The commercially available hydrogels are quite expensive and not many companies are currently manufacturing them. Hydrogels are being extensively used/produced in the US, UK, Australia, and Israel, but their use in the Indian agricultural sector is quite limited, owing to limited production (0.001% of all the Indian agricultural products).
INCEPTION
The innovative hydrogel idea was conceived by Dr. Patel while reviewing baby products (baby diapers). Hydrogels are extensively used in diapers. Dr. Patel started to work on hydrogels and successfully devised a hydrogelling system with agricultural implications. The effective use of hydrogels can reduce the water and fertilizer requirements for crops.










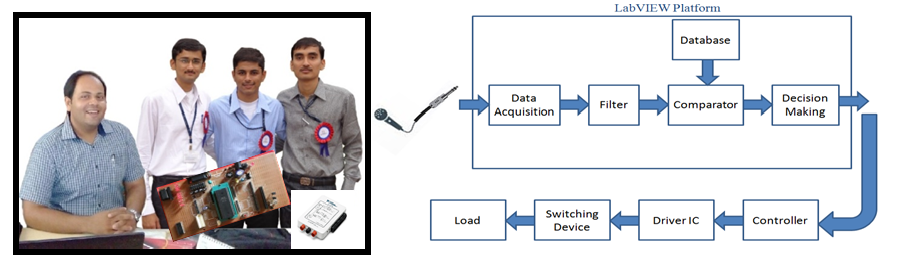
Mr. Arjav Bavarva (Assistant Professor, Dept. of Electronics and Communication) and his students (Rahul Vyas, Parth Gangadia, and Faizal Panavadhu) have developed a sound-operated device control system at RK University’s School of Engineering. The developed system responds to pre-defined speech commands (from a training database) and performs specific functions. The functionality of this versatile device is likely to be improved further in the near future. The device has already been signal correlated. Therefore, language is not expected to act as a barrier. The existing prototype incorporates a microcontroller and it has been designed with the help of the software LabVIEW. Future plans include improving the accuracy and the signal to noise ratio. The team got its inspiration from the Hollywood movies “Ironman” and “Players.” This project has several implications for national security. It is expected to offer immense help to physically challenged people.
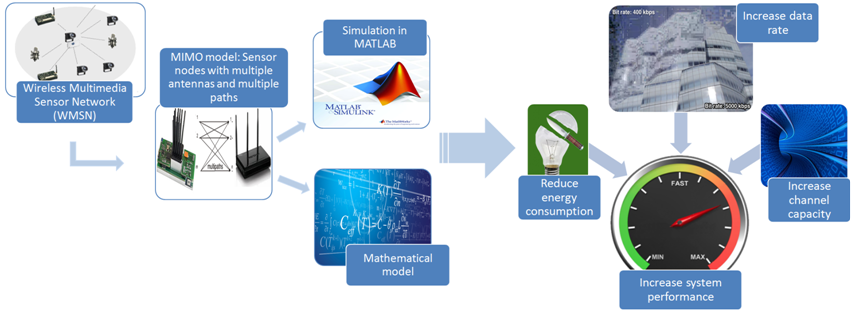
Wireless Multimedia Sensor Networks (WMSN) are designed to transmit audio and video streams, still images, and scalar data. Multimedia transmission over wireless sensor networks has many promising applications such as video surveillance systems, object tracking, telemedicine, theft control system, and traffic monitoring. Researchers face many challenges, including a higher data rate, lower energy consumption, lower reliability, reduced signal detection/estimation, and an uncertainty in the network topology. In order to make various applications of WMSN useful, certain issues pertaining to the quality of service and security also need to be addressed. Multiple Node Multiple Input Multiple Output (MN-MIMO) properties have been used to improve system performance in terms of data rate, energy consumption, and channel capacity. Mr. Arjav Bavarva and his student Ms. Preetida Jani (Dept. of Electronics and Communication) have employed a mathematical model for calculating and analyzing the various network parameters including SNR, channel capacity, and data rate. Simulation results demonstrate the effect of various channel models on the output in a deep fading environment and the proposed channel model performs better for WMSN than for non-adaptive systems, in terms of the bit error rate.
.png)
Mr. Ghanshyam Tejani (Dept. Of Mechanical Engineering) is working on an improved version of teaching-learning based optimization (TLBO) with static and dynamic constraints, for truss topology optimization (TTO). He has been focusing on improving the basic TLBO algorithm in order to enhance its exploration and exploitation abilities, by giving due consideration to variables such as the number of teachers, the adaptive teaching factor, tutorial learning, and self-motivated learning. Moreover, the structural optimization problems under consideration have multiload conditions and are subjected to the constraints for natural frequencies, element stresses, nodal displacements, Euler buckling criteria, and kinematic stability conditions. The TTO is achieved with the removal of the superfluous elements and nodes from the ground structure, thereby resulting into the conservation of mass. In this method, several difficulties arise due to singular solutions and unnecessary analysis. Therefore, the finite element model is reformed in an attempt to resolve these difficulties. In addition, a single-stage optimization approach is used whenever size and topology optimization is considered simultaneously. The results of the modified sub-population TLBO (MS-TLBO) are comparable to those obtained using other state-of-the-art algorithms.
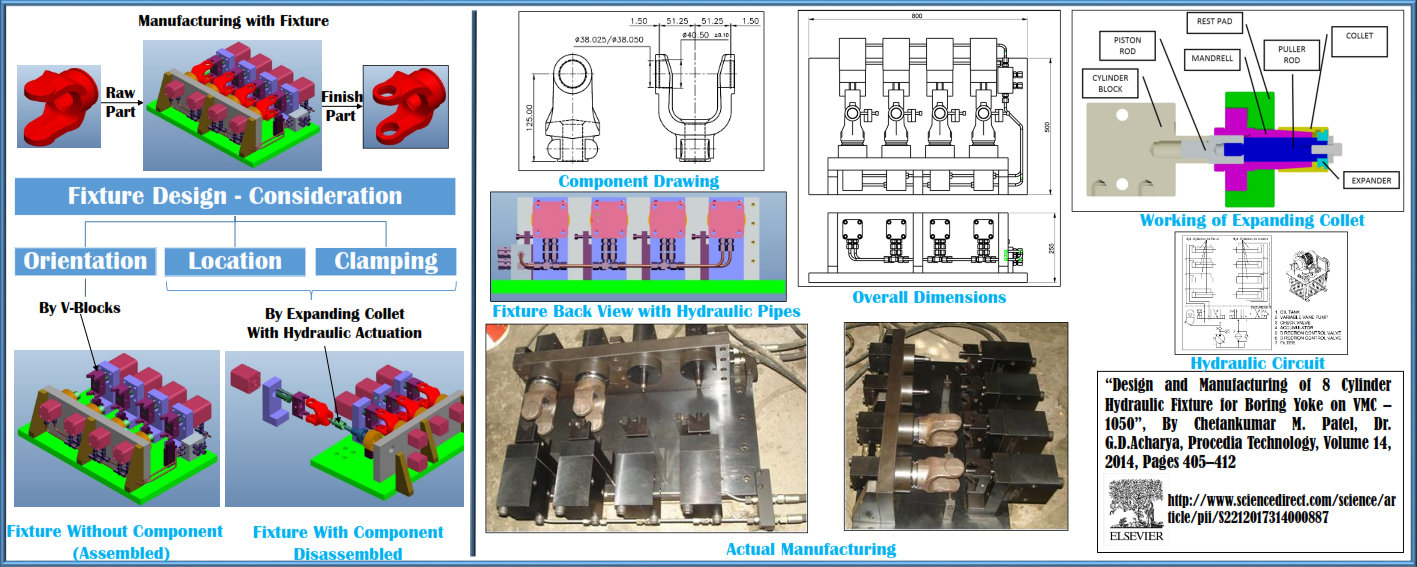
Jigs and fixtures are the special production tools that constitute standard machine tools. These specialized machine tools are quite versatile in nature. They are normally used in large scale production by semi-skilled operators; however they are also used in small scale production whenever interchangeability is required. Various aspects pertaining to the design of fixtures have already been discussed in literature. However, there is a need to combine all of these research findings into an industrial application. Mr. Chetal Patel from the Dept. of Mechanical Engineering is currently working on the design and manufacture of an eight-cylinder hydraulic fixture for boring YOKE on VMC-1050. Prof. Patel has adopted a functional approach for designing the fixture. The hydraulic as well as collet fixtures incorporate an expanding (customized) collet as the main element. The corresponding design decreases the overall production time to a significant extent.
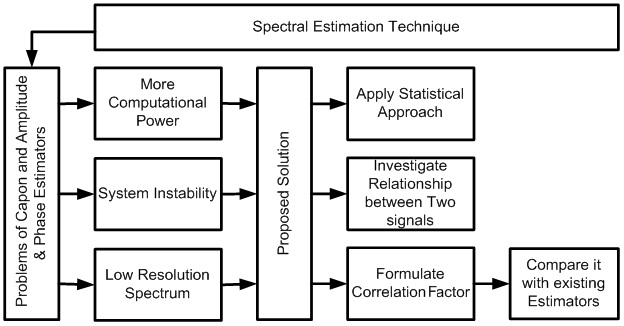
Capon and APES (Amplitude and Phase Estimation) techniques are one of the most frequently used spectral estimation techniques in the area of signal processing. These techniques provide smoother features to the signals and can potentially assist investigations in the area of signal processing. However, both the estimation techniques need heavy processing and computational power and suffer from high system instability as well as lower resolution of the spectral analysis. The current study presents a non-parametric approach and uses statistical measures to enhance the spectral estimation techniques. The work focuses on designing new spectral estimation techniques using conventional filter-bank decomposition methods and enhances it further using statistical approaches. The study also introduces a parameter called as the “Correlation Factor,” which performs the evaluation of potential frequency domains between the two signals. After comparing the outcome of our spectral estimation technique with that of the existing spectral estimation techniques (e.g. Periodogram, PWelch, and Multitaper techniques), it is found that our proposed system results into a significantly enhanced performance. This study (being carried out by Mr. Kantipudi, Asst. Prof., Dept. of Electronics & Communications, RK University) may potentially provide a highly comprehensive baseline for signal processing during spectral estimation, thereby enriching the academic experience of new engineering entrants.
